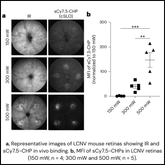
Using CHP to Understand Cardiac Fibrosis Pathology and Therapeutic Efficacy
Following a Myocardial Infarction (MI), the heart relies on myofibroblasts to deposit collagen, creating a vital "patch" to maintain structural integrity. However, when this process becomes chronic, excessive collagen deposition leads to cardiac fibrosis—a primary driver of heart failure. For researchers, the goal is to find therapies that limit this pathological remodeling without compromising...
View Details
Visualizing Cardiac Fibrosis: How Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs) Reveal Remodeling
Heart disease is the largest cause of death in the world. A major driver of heart disease is angiotensin II, a hormone that, if dysregulated, can trigger inflammation and fibrosis in the heart. Previously, it had been shown that CD14+ derived myeloid angiogenic cells (MACs) have the ability to drive angiogenesis. However, the utility...
View Details
Decellularization Induces Hierarchical Disorganization in Ligament Scaffolds
Ligament injuries, particularly those affecting the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) or Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL), present a significant orthopedic challenge due to the tissue's poor vascularization and limited regenerative capacity. Decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) scaffolds have emerged as a promising solution, offering a natural framework that minimizes immune rejection while theoretically preserving the native...
View Details
CD206+IL-4Rα+ Macrophages Are Drivers of Adverse Cardiac Remodeling in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Myocardial infarctions (MI), or more commonly known as heart attacks, have prolonged health implications that affect millions worldwide. Chronic heart failure (HF) is very common after a heart attack, with about 20-30% of patients developing it within a year. Heart failure after MI is characterized by distinct structural, cellular, and molecular changes that differentiate...
View Details
Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs) Elucidate Ursolic Acid's Efficacy in Collagen Homeostasis
Tissue fibrosis, pathologically characterized by the excessive and dysfunctional deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, notably collagen, remains a significant challenge in chronic disease management. Fibrosis accounts for nearly half of all mortality in the United States. Effective therapeutic strategies must engage a dual mechanism, simultaneously arresting neo-collagenesis and actively degrading existing, pathological collagen...
View Details
CHPs Contribute to Abdominal Aortic Anurrysm (AAA) Research)
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is a life-threatening condition characterized by the extensive remodeling and breakdown of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Understanding the factors governing aortic instability - particularly the micro/nanoscale changes - is paramount for improving AAA management. A new publication, "Nano-mechanical Mapping of Human and Porcine Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm" uses advanced imaging techniques...
View Details
CHP Staining: Unlocking a New Therapeutic Strategy for Fibrosis
Fibrosis, the pathological accumulation of collagen and other ECM components, is a major health concern implicated in an estimated ⅓ of all natural deaths. While current anti-fibrotic drugs aim to slow progression, advanced fibrosis is often left untreated, leaving transplantation the only remaining option in many cases. A new therapeutic approach is focusing on...
View Details
Damaged collagen detected by collagen hybridizing peptide as efficient diagnosis marker for early hepatic fibrosis
Liver fibrosis, a significant pathological consequence of chronic liver disease and damage, is characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. This build up of non-functional scar tissue progressively replaces healthy tissue in the liver, leading to conditions such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and heightened risk of liver cancer. With a high...
View Details