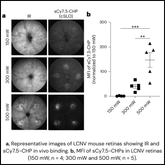
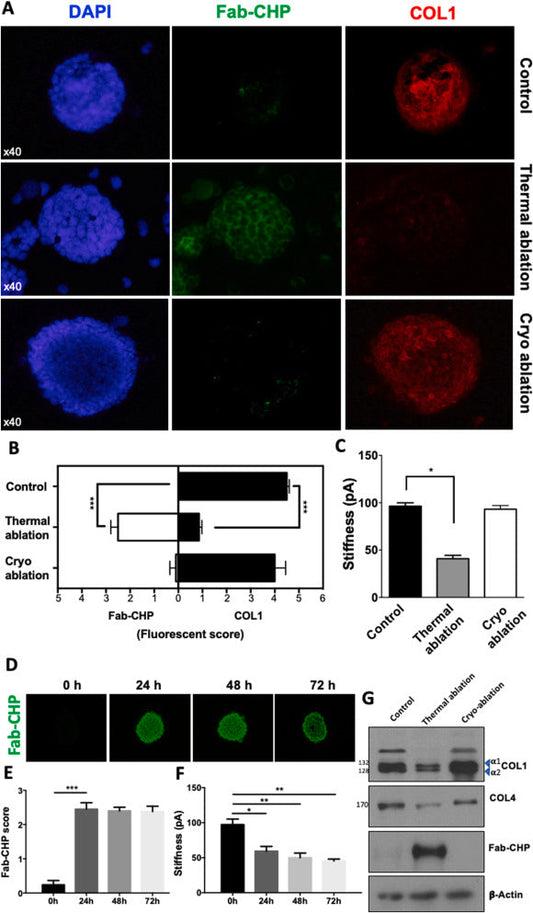
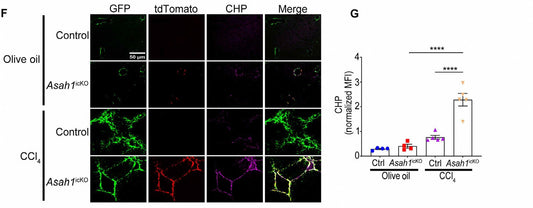
Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs): Unraveling the role of Denatured Collagen in Neuroblastoma.
The complex interplay between the tumor microenvironment (TME) and cancer progression is a critical area of research, particularly in aggressive childhood cancers like neuroblastoma (NB). A recent study, “Unraveling the Role of Denatured Collagen in Neuroblastoma via Collagen Hybridizing Peptides,” published in July 2023, has shed light on the impact of thermal ablation on...
View Details
Resolving fibrosis by stimulating HSC-dependent extracellular matrix degradation
Fibrosis is not just characterized by extracellular matrix (ECM) component deposition, but it’s better described as an imbalance between the production and breakdown of the ECM. Current treatments for fibrosis largely focus on stopping ECM production, but there is a significant, untapped potential in promoting its breakdown. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are enzymes that degrade...
View Details
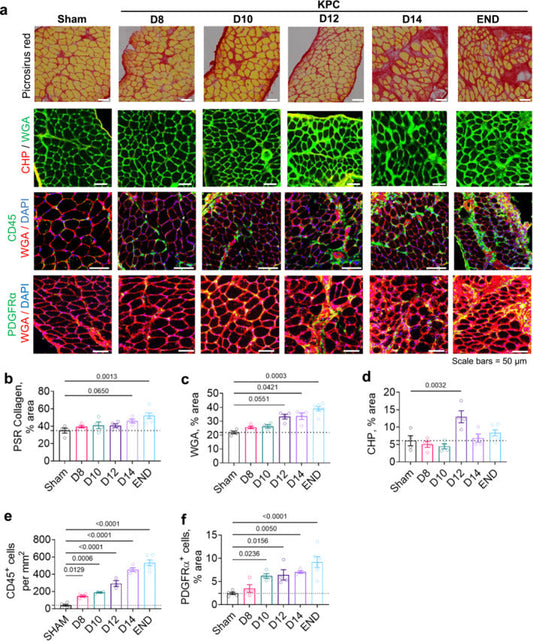
Pinpointing Fibrosis: How Collagen Hybridizing Peptides Illustrate Muscle Wasting in Pancreatic Cancer
Muscle wasting in cancer is estimated to contribute to approximately 30% of cancer-related deaths, with a deterioration of respiratory muscles implicated as a major cause of mortality. One of the most lethal cancers, Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), also has the highest prevalence and earliest onset of cachexia of all cancers. While researchers knew that...
View Details
Can Physical Cues Prevent Scarring? Using CHPs to Investigate Myofibroblast Behavior
The link between tissue architecture and function is pivotal for the human cornea to properly function, since a highly organized collagen matrix is essential for optical transparency and vision. Following an injury to the cornea, aberrant healing results in a disorganized matrix which impedes light transmission through the cornea and leads to vision loss....
View Details
A Novel Collagen Hybridizing Peptide for Activating LAIR-1 Inhibitory Pathway at Damaged Collagen Sites
ABSTRACT TITLE: A Novel Collagen Hybridizing Peptide for Activating LAIR-1 Inhibitory Pathway at Damaged Collagen Site AUTHORS: Regan Stephenson, Bridget Glass, Kyle Dunlap, Mallory Longacre, Lucas Bennink, Mike Kirkness AFFILIATIONS: 3Helix, Inc, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA ABSTRACT: Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 1 (LAIR-1), an inhibitory collagen receptor expressed on a variety of immune...
View Details
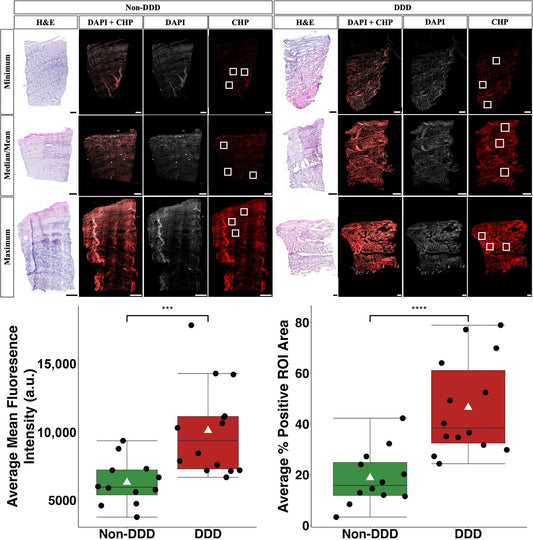
How Collagen Hybridizing Peptides Reveal Hidden Molecular Damage Behind Back Pain
Hundreds of millions of people suffer from chronic back pain, often stemming from Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD). MRI imaging can visualize the structural decay of spinal discs, but what if DDD pathogenesis starts long before gross morphological degeneration is identified? For years, researchers have hypothesized that the real issues begin on the molecular level...
View Details
Wound healing breakthrough: How Collagen Hybridizing Peptides turn damaged tissue into a target for drug delivery.
Wound infections pose a major risk to recovery, having the potential to turn otherwise minor injuries into severe medical challenges. Scientists have continued to investigate the potential of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) for their ability to kill a broad spectrum of microbes while mitigating the risk of increasing microbe resistance. While powerful, AMPs do have...
View Details
Shedding Light on Cardiac Repair: How Red-Light Preconditioning Improves Cell Therapy
Following a heart attack, fibrosis is the primary obstacle to recovery. Healthy heart muscle is replaced with non-functional scar tissue, which stiffens the heart wall and leads to chronic heart failure. While therapies have been investigated, cell-based therapies have failed to resolve this issue, as transplanted cells do not survive or engraft effectively in...
View Details