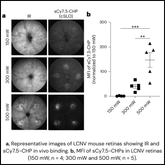
Using CHP to Understand Cardiac Fibrosis Pathology and Therapeutic Efficacy
Following a Myocardial Infarction (MI), the heart relies on myofibroblasts to deposit collagen, creating a vital "patch" to maintain structural integrity. However, when this process becomes chronic, excessive collagen deposition leads to cardiac fibrosis—a primary driver of heart failure. For researchers, the goal is to find therapies that limit this pathological remodeling without compromising...
View Details
Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs) Elucidate Ursolic Acid's Efficacy in Collagen Homeostasis
Tissue fibrosis, pathologically characterized by the excessive and dysfunctional deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, notably collagen, remains a significant challenge in chronic disease management. Fibrosis accounts for nearly half of all mortality in the United States. Effective therapeutic strategies must engage a dual mechanism, simultaneously arresting neo-collagenesis and actively degrading existing, pathological collagen...
View Details
CHPs Contribute to Abdominal Aortic Anurrysm (AAA) Research)
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is a life-threatening condition characterized by the extensive remodeling and breakdown of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Understanding the factors governing aortic instability - particularly the micro/nanoscale changes - is paramount for improving AAA management. A new publication, "Nano-mechanical Mapping of Human and Porcine Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm" uses advanced imaging techniques...
View Details
Visualizing Mast Cell-Driven Collagen Damage in nAMD Progression
Collagen Hybridizing Peptides track mast cell-driven collagen remodeling & degradation in neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration (nAMD) research. Explore the study's key insights and learn about how you can target damaged collagen for insights in your research!
View Details
Collagen Hybridizing Peptides Validate a Novel Bone Organoid Model
Validate collagen integrity in your biomaterials with 3helix CHPs. Discover how Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs, 3Helix Inc.) ensure reliable data in tissue engineering and bone remodeling research.
View Details
Beyond Fibroblasts: CHPs provide Key Evidence for Keratinocyte-Driven Skin Development
Collagen is skin's foundation, but how it's truly built has been hidden – until now. Discover how see-through axolotls are providing an unprecedented window into this process, revealing secrets that could reshape skin science.
View Details
First Empirical Evidence of Collagen Damage during Bone Fracture
Bone is a remarkable material, strong enough to withstand impressive forces without fracturing. Despite decades of research, however, our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying bone’s fracture resistance has remained incomplete. It has long been hypothesized that collagen degradation occurs following bone fracture. Until recently, this hypothesis lacked empirical evidence due to a...
View Details
Skeletal muscle fibrosis is associated with decreased muscle inflammation and weakness in patients with chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) progressively impairs kidney function, affecting millions. Beyond kidney-related complications, patients often experience muscle weakness and reduced mobility, begging the question: does muscle fibrosis contribute to those limitations? Figure 1 demonstrates a significant increase in collagen deposition within the vastus lateralis muscle of CKD patients. Histochemical analysis using picro-sirius red...
View Details