Unveiling Collagen Organization: The role of CHPs in understanding COL6-Related Dystrophies
Collagen VI-related dystrophies (COL6-RDs) are a group of genetic muscle disorders impacting both children and adults. These conditions can lead to delayed motor development, progressive muscle weakness, joint contractures, and respiratory complications. In severe cases, COL6-RDs result in the loss of independent mobility and a reliance on ventilatory support. Given the profound impact on...
View Details
Insights into Collagen Damage and Spine Stiffness: Unraveling the Role of Oxidative stress in Scoliosis
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is the most prevalent pediatric spine disorder, affecting 3-4% of children worldwide. It develops in the absence of obvious congenital or physiological defects. While some evidence suggests a genetic correlation, the underlying biological causes remain largely unknown. Without a comprehensive understanding of AIS at a biological or physiological level, treatments...
View Details
Understanding ECM Remodeling in Full-Thickness Skin Grafts: Insights from Collagen Hybridizing Peptide Staining
Full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs) are commonly used in surgeries like hernia repairs, but how they integrate and heal long-term is still not fully understood. A recent study focused on extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and the role of fibroblasts in skin graft healing. Using collagen hybridizing peptide (CHP) staining, researchers observed active collagen turnover in...
View Details
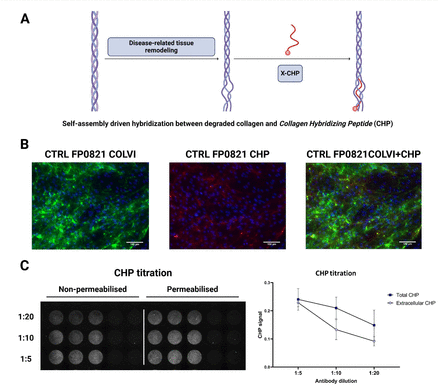
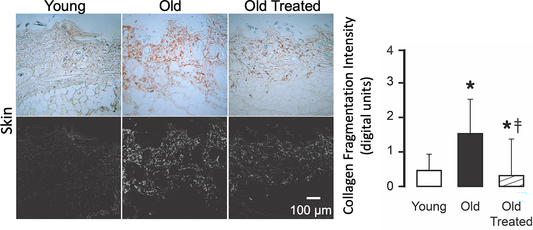
Aging Unveiled: CHPs Reveal Widespread Tissue Damage and Reversible Collagen Breakdown in Aged Mice
Staining of collagen in multiple organs with Biotin-conjugated Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (B-CHPs). The black and white panels are an extraction of the fluorescent peptide signal, used for quantification of collagen damage. The universal process of aging involves the dysregulation of a wide spectrum of biological mechanisms. Using mouse models, DeLano et....
View Details
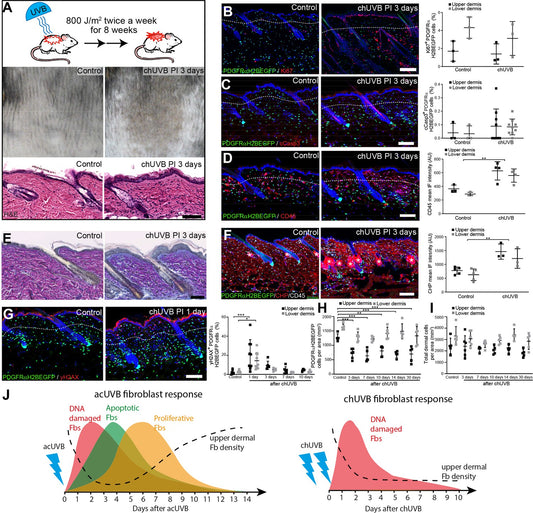
Understanding Collagen Hybridizing Peptides in Assessing Dermal Damage and Repair After UV Exposure
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) occurs during prolonged exposure to sunlight and is associated with a variety of negative physiological effects, including skin damage, inflammation, and cancer. Many of these effects are due to the formation and accumulation of reactive oxygen species, which damage the extracellular matrix and impair cellular functioning. Fibroblasts are the...
View Details
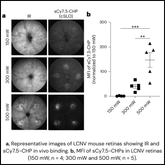
Revolutionizing AMD Research with CHPs: In Vivo Detection of Subretinal Fibrosis with Collagen Hybridizing Peptides
Subretinal fibrosis, the formation of disorganized collagen scar tissue underneath the retina, is often associated with neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration (nAMD). Current nAMD diagnostic methods rely on Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), which provides structural imaging, but lacks the sensitivity to distinguish collagen from other subretinal ECM components. This limitation leaves a gap in evaluating...
View Details
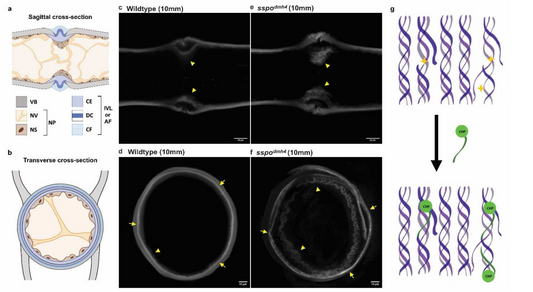
Advancing Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Assessment with Collagen Hybridizing peptides: A Fast, Accurate Approach for Research and Clinical Applications
Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration is a significant contributor to lower back pain, a leading cause of disability in individuals over 45. IVD is marked by the degradation of collagen and the extracellular matrix, which triggers inflammatory responses, recruits macrophages, and accelerates degeneration. Monitoring the progression of IVD degeneration and assessing the effectiveness...
View Details
Targeted Drug Delivery in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Leveraging Collagen Hybridizing Peptides for Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy
Histological staining of mouse tibia-talus joints showing healthier articular cartilage due to iFab-CHP treatment compared PBS placebo. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease which leads to the breakdown of the cartilage in the synovial joints. Current treatment strategies with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFa) targeting neutralizing antibodies effectively reduce...
View Details