Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs) Elucidate Ursolic Acid's Efficacy in Collagen Homeostasis
Tissue fibrosis, pathologically characterized by the excessive and dysfunctional deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, notably collagen, remains a significant challenge in chronic disease management. Fibrosis accounts for nearly half of all mortality in the United States. Effective therapeutic strategies must engage a dual mechanism, simultaneously arresting neo-collagenesis and actively degrading existing, pathological collagen...
View Details
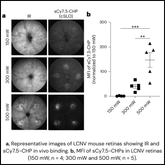
Damaged collagen detected by collagen hybridizing peptide as efficient diagnosis marker for early hepatic fibrosis
Liver fibrosis, a significant pathological consequence of chronic liver disease and damage, is characterized by the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. This build up of non-functional scar tissue progressively replaces healthy tissue in the liver, leading to conditions such as cirrhosis, liver failure, and heightened risk of liver cancer. With a high...
View Details
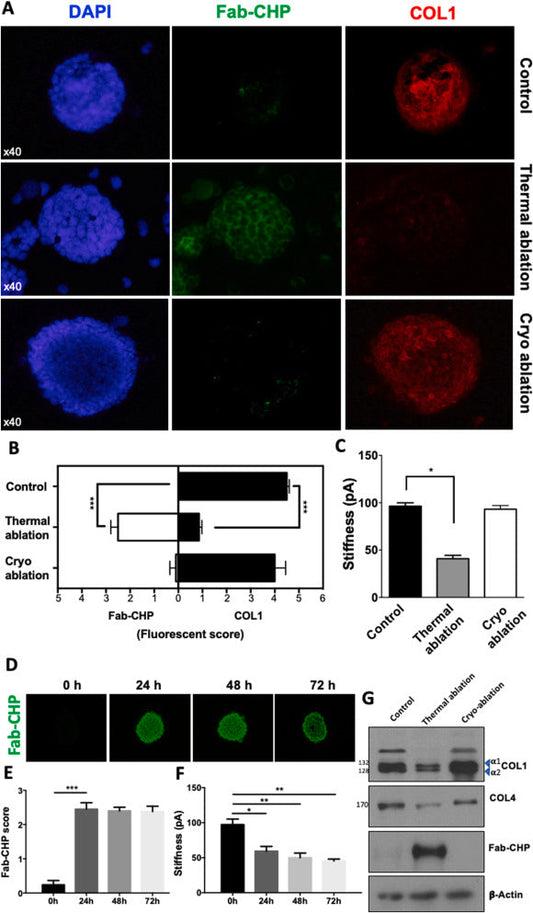
Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHPs): Unraveling the role of Denatured Collagen in Neuroblastoma.
The complex interplay between the tumor microenvironment (TME) and cancer progression is a critical area of research, particularly in aggressive childhood cancers like neuroblastoma (NB). A recent study, “Unraveling the Role of Denatured Collagen in Neuroblastoma via Collagen Hybridizing Peptides,” published in July 2023, has shed light on the impact of thermal ablation on...
View Details
Beyond Fibroblasts: CHPs provide Key Evidence for Keratinocyte-Driven Skin Development
Collagen is skin's foundation, but how it's truly built has been hidden – until now. Discover how see-through axolotls are providing an unprecedented window into this process, revealing secrets that could reshape skin science.
View Details