CHP Staining: Unlocking a New Therapeutic Strategy for Fibrosis
Fibrosis, the pathological accumulation of collagen and other ECM components, is a major health concern implicated in an estimated ⅓ of all natural deaths. While current anti-fibrotic drugs aim to slow progression, advanced fibrosis is often left untreated, leaving transplantation the only remaining option in many cases. A new therapeutic approach is focusing on...
View Details
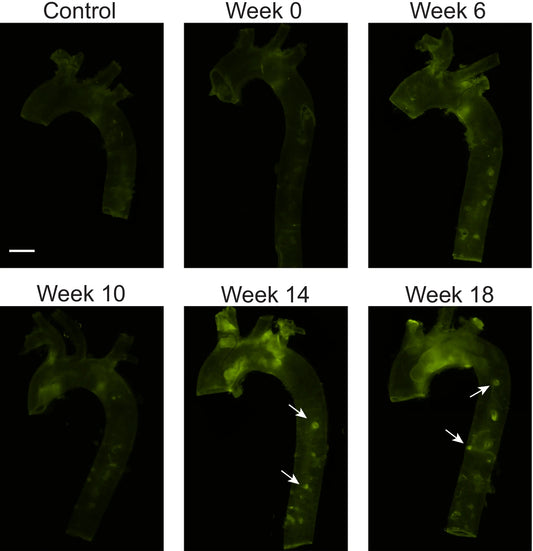
First Empirical Evidence of Collagen Damage during Bone Fracture
Bone is a remarkable material, strong enough to withstand impressive forces without fracturing. Despite decades of research, however, our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying bone’s fracture resistance has remained incomplete. It has long been hypothesized that collagen degradation occurs following bone fracture. Until recently, this hypothesis lacked empirical evidence due to a...
View Details
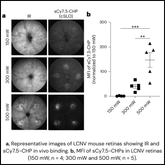
Detecting Early Arterial Damage in Atherosclerosis: How Collagen Hybridizing Peptides Overcome Diagnostic Challenges
Atherosclerosis, characterized by the buildup of plaque inside human arteries, is one of the leading causes of cardiovascular diseases. The disease is brought on by a complex interplay between lipids, inflammatory cells, and the ECM. Arterial blood flow is restricted as plaques form, which can rupture to cause blockage. Arterial blockage, or occlusion, is...
View Details